With our minds turned to efficiency and cost considerations, the increasing density of warehouse storage space brings its own set of challenges. To increase and maximize storage, warehouse owners and operators can choose to change the pallet rack height. This change would let them accommodate more beam levels throughout the racking system.
However, this new setup should also consider the pallet racking depth: The height-to-depth ratio is a significant factor affecting the stability of racking installations. After all, a tall rack serves no purpose if it is going to topple over.
What is the height-to-depth ratio?
RMI (Rack Manufacturers Institute) defines the height-to-depth ratio for a single row of pallet rack as follows. The distance from the floor to the top surface of the highest load-supporting beam level is divided by the depth of the frame.
Section 8.1 of RMI’s ANSI MH16.1: Specification for the Design, Testing and Utilization of Industrial Steel Storage Racks advises evaluating the height-to-depth (HTD) ratio to determine the stability of a single row of standard steel storage rack.
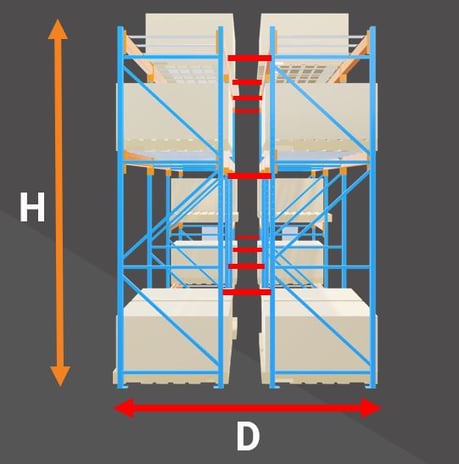
How to determine your pallet rack's height and depth ratio
As a rule of thumb, use this formula to avoid the instability of your racking system:
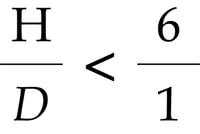
H = Height – measured from floor to the top surface of the highest-supporting beam level
D = Depth – measured along the floor, from the outside of the front column to the outside of the back column.
If the height (H) of the racking system divided by the depth (D) of the frame is beyond 6, the rack design engineer must take special measures to prevent overturning, like adding row spacers, for example.
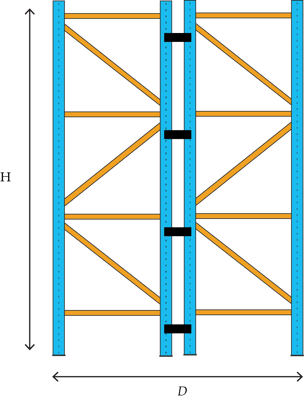
For instance, a pallet rack height is 240”, calculated from floor to top surface of the highest load-supporting beam level. This number is divided by 42″, which is the pallet racking depth of a standard upright. The ratio is then 5.714. It does not exceed 6, therefore it’s considered an acceptable ratio, within 6 to 1, needing only normal anchoring. If two systems are placed back-to-back and are not attached with a row spacer, their depths should be calculated individually as a single row (see the left side of figure 1).
If the same 42″ deep frame is 24′ tall, this would result in a ratio of 7:1, and additional measures should be incorporated to further secure the rack and avoid possible overturning.
Additional measures to stabilize your pallet rack
Row spacers
As already mentioned, one option is to add row spacers to connect rows of uprights and maintain even spacing between racks. Placing rows of racks in a back-to-back configuration and connecting them with row spacers will greatly increase stability.
Pallet rack anchors
Adding anchors will stabilize the rack and diminish the risk of upright displacement. The choice of anchors must be approved by a professional engineer. Installing larger baseplates will also allow better load distribution to the ground, with more space to anchor the frame.
Cross-aisle or overhead ties
Adding cross-aisle or overhead ties to connect the topmost sections of the upright frames that span across an aisle can also prevent overturning. This is recommended by ANSI MH16.1 if the height-to-depth ratio exceeds 8 to 1.
Following the height-to-depth ratio: a simple rule of thumb to improve safety
This rule of thumb mentioned above is meant for standard rack frames arranged in a single row. It does not apply to racks with cantilevered uprights or columns that are set back at their base. Whenever you want to make changes to the configuration of your storage pallets or the racks supporting them, you should consult a specialized rack design engineer.
If you would like to book a warehouse inspection or simply speak with one of Damotech's rack safety experts, click here. Remember that saving space could compromise safety. Following the pallet rack height-to-depth ratio keeps everyone on the safe side. Making well-informed choices will help you ensure your rack's stability.












