Learning to anchor pallet racks is akin to mastering the art of constructing skyscrapers. Just as skyscrapers rely on being securely anchored to bedrock to withstand formidable lateral wind and seismic forces, the stability of a rack system hinges on its anchors. Much like a skyscraper’s foundation determines its resilience, the connection of a rack system to the concrete floor is paramount for ensuring stability.
How to Anchor Pallet Racks: Quick Tip
First, ensure the racking is plumb and square to anchor pallet racks securely. Insert wedge bolt anchors into the holes and tap them with a mallet until the washer and nut contact the base plate. Finally, a torque wrench is used to tighten the nut to the specified torque, ensuring the anchor’s proper installation and stability. Always follow OSHA pallet rack anchor requirements.
Read this article for more detailed instructions and reasons why proper anchoring matters.
At Damotech, we have engineered racking repair systems stronger than the original structures being replaced, the strongest in the industry. Everyone involved with racking installation, maintenance, and repair must understand pallet rack anchoring standards to properly anchor racks to the floor and achieve engineered ratings.
Pallet Rack Anchors and Warehouse Rack Collapse
Ng, Beale, and Godley found in their analysis of rack failures that anchors can play a big role in converting a localized collapse into the “domino” effect or “unzipping” of the structure for an entire rack system. This is known as a “progressive collapse” of a racking structure. In their computer static and dynamic analyses, these engineers found that:
3.3…whenever [other joints] or base plate connections reached their maximum tensile yield forces they were assumed to have failed….
Understanding how to anchor pallet racks is crucial for ensuring structural integrity, particularly during unexpected loads, damage, or partial collapse. While delving into the intricacies of this subject is recommended for a comprehensive grasp (reading the paper is recommended), the essence is clear: the effectiveness of the anchors and the plates they secure to the floor is paramount. Should the pallet rack anchors fail due to improper installation, damage, or the utilization of unsuitable anchors, the racks are more susceptible to collapse. Such failures typically occur after an initiating event, such as beam-column joint failure, uneven loading, seismic activity, or even impact from a forklift.
Therefore, anchor bolt selection and proper installation are critical in anchoring pallet racks.

Expected Loads
Real-world loads for pallet rack components are a complex topic. The rack components operate as a system, and rack failures often are primed by multiple system factors before a collapse. The load applied to the pallet rack anchors is vital when choosing or replacing anchors during rack repairs. All racking will experience real-world loads that will try to pull out or shear the anchor bolts for pallet racking used to connect the base plates to the concrete floor. This happens when stocks are being stored or removed, when unexpected load shifting occurs, when accidental forklift strikes occur, and when there is any seismic activity. Regular racking inspection should always include a professional inspection of all rack anchors.
Concrete anchor systems used to anchor pallet racking will experience two types of loads:
-
TENSION : Where the rack is trying to “lift” the column, pulling on the fastener vertically. Seismic activity can also create tension as the ground heaves vertically and drops suddenly.
A lateral force on the rack above the floor can also create tension. When these lateral loads are offset from the floor by distance, one side’s base plates become the pivot, and the opposite side’s base plates get lifted… a “tipping” force. This lateral force can come from a forklift strike or pallet loading and unloading that does not clear the beams or shelving.
The distance from the floor acts as the moment arm to create leverage and increase the pull on the anchor. Essentially, the higher the point of impact of the lateral force, the longer the moment arm will be. This will cause greater torque to act on the system and more tension at the anchor.
Seismic activity
can also create uplift tension forces on anchors, causing them to experience a rocking motion. Taller rack systems, especially ones with uneven load distribution, will greatly experience these effects and place a lot of tensile stress on the anchors. If seismic forces are strong enough, there are also overturning risks, which can cause the anchors to be pulled out completely. This is another reason why it is mandatory to ensure anchoring is done correctly and up to standard.
-
SHEER : This is where the column tries to shift laterally, typically from a forklift strike, creating a horizontal force right where the base plate meets the concrete. That force is concentrated at this point like a pair of snips cutting steel—creating immense force across the shaft of the fastener. Even if these impacts do not cause a failure right away, it could cause the anchor to loosen, reducing its effectiveness and leading to further risks. Again, lateral seismic shaking can also create sheer stress on the anchors, causing them to shear off or loosen over time.
Both tension and sheer for a fastener are given a “usable rating,” which is the approved, usable tension, or sheer. Most anchor manufacturers use a safety factor of 2.5 to determine the maximum failure rating. A safety factor of 2.5 is commonly used in structural applications but can vary depending on the situation. This is why it is essential to consult with a qualified engineer . For example, if a fastener has an ultimate strength of 25,000 Ib, applying a safety factor of 2.5 would result in a usable sheer rating of 10,000 Ib. This means the fastener should not be used in applications where the expected sheer force exceeds 10,000 Ib.
Those loads at the pallet rack anchors transfer from the columns attached to the footings. For rack repairs , it is essential to ensure that the newly repaired structure attached to the anchors is as strong as or stronger than the original structure.
How to Anchor Pallet Racks? Which Type of Pallet Anchor?
When considering how to securely anchor pallet racks into concrete, one encounters many anchor options. However, in the context of typical operating environments for pallet racks, two primary choices are commonly employed: strike wedges and wedge bolts. Each option comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Strike Anchors
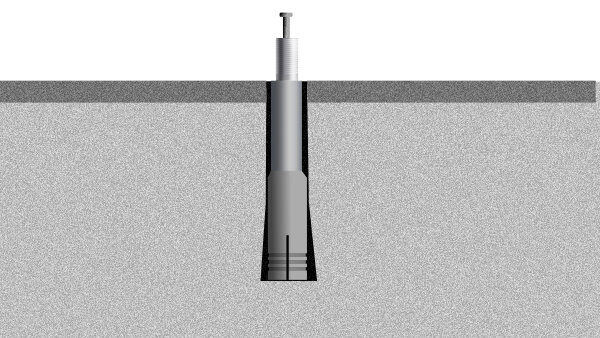
Strike anchors have a sturdy pin inside a sleeve with a wedge at the bottom. When struck by a mallet, they expand in the concrete hole, driving a pin to expand the bottom of the wedge into the concrete. Strike anchors are easy to install and can be removed easily by prying up the pin. However, they must be replaced if removed and typically have half the ultimate tension and shear ratings of our next fastener, bolt wedges. For this reason, strike anchors are not recommended.
Wedge Bolts
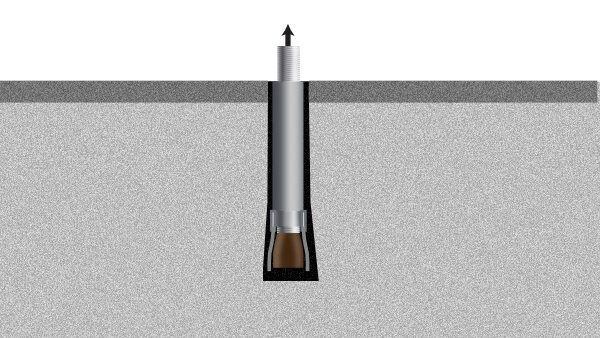
Wedge bolts hit the sweet spot of ease of installation, strength, and higher embedment depths than strike anchors, further increasing tension ratings.
Wedge bolts have a wedge at the bottom attached to the main bolt. The top of the bolt/stud has a nut and washer that must be tightened to the manufacturer’s torque specification. The anchor bolt is driven into the concrete hole with a mallet until the depth when the nut and washer contact the base plate. After contacting the base plate, a wrench tightens the nut until it has the correct torque. That torque is specified to open the wedge enough to achieve the engineered tension capacity. Wedge bolts must have precise hole sizes (the same as their diameter when using ANSI-sized bits) and be torqued to the manufacturer’s specification to achieve their engineered ratings.
Wedge bolts are designed as “slip” anchors when the anchor has been subjected to a force that exceeds the maximum usable load, the anchor nut is loose, and the anchor remains more than 50% in the hole. They can be driven or pounded back into the hole and retightened to the specified torque, reestablishing the rated tension.
For these reasons, we only use wedge bolt anchors when repairing damaged rack columns using Damotech’s engineered solutions due to the high-impact environments in which repair kits are installed.
Base Plates

Most racking base plates come with multiple holes to allow for various bolt placements. If we hit rebar when drilling, we’ll need to select a different hole.
When learning how to anchor a pallet rack column to the concrete floor, following the OEM requirements for the number of pallet rack anchors and fastener specifications is essential. The base plate holes are typically 9/16", 11/16", or 13/16" for 1/2", 5/8", or 3/4" anchors, depending upon the rack manufacturer’s engineering specifications.
It is critical to space out the anchors and not place them too close together. For recommended anchor spacing, refer to the manufacturer.
Thicker Steel Foot Plates Increase Impact Resistance

Understanding how to anchor pallet racks involves considering the thickness of the steel used in the anchor plate, which is a critical factor. Opting for thicker steel foot plates enhances the shear resistance of the anchors. Increased shear resistance directly correlates with greater impact resistance for the entire rack system. Additionally, it’s essential to select a foot plate that complies with potential seismic engineering standards applicable in your region, often necessitating an even larger and sturdier footplate. Generic parts may not adequately fulfill all these requirements.
How to Anchor Pallet Racks with Embedment Depth
Wedge bolts have a tension rating that increases with embedment depth. Of course, the longer the bolt, the deeper the embedment. The deeper the embedment, the stronger the tension rating. Embedment depth increases the usable tensile strength of the wedge bolt. Concrete is strong and typically a minimum of 6" deep but is weakest in shear. As a bolt is pulled vertically, strain lines create internal shear from the bottom of the wedge to the top of the concrete. You can think of these strain lines running in various angles up to 45 degrees from the vertical of the bolt hole. The concrete in this zone provides strength against pull-out.
The depth of the embedment is directly correlated to the radius of the inverted conical area. Essentially, a larger embedment depth means a much greater capacity.
How to Anchor Pallet Racks with Anchor Spacing
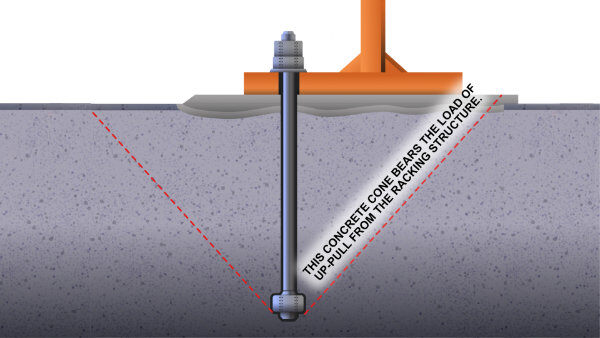
Concrete anchors are only as strong as the concrete to which they attach. Because concrete is brittle in sheer, there needs to be a significant distance between each anchor to provide enough concrete surrounding each fastener. Furthermore, fasteners can create combined loads on concrete, so they need to be far enough apart that these loads don’t degrade the tension ratings of the bolts based on a diminishment of the anchoring due to combined loads.
Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s requirements for your anchor spacing.
How to Install Pallet Rack Anchors
The following best practices should be used when installing wedge bolt anchors:
- Before anchoring, ensure the racking and engineered repair kits are plumb and square. Any changes in the racking may affect the bolt location.
- Use the hole pattern in the base plate as a drilling template.
- Drill holes utilizing a hammer drill and the correct carbide masonry bit. Be cautious not to damage the base plate or drill through it. The drill bit diameter should be the same as the wedge anchor.
- Next, clear out the holes. A vacuum or compressed air is easiest.
- Place the washer onto the anchor bolt stud and thread the nut on the bolt.
- Insert the assembled wedge bolt anchors into the drilled anchor holes.
- Using a hammer or mallet, cautiously pound the anchors into the hole until the washer and nut contact the base plate.
- Go back and tighten each nut using a torque wrench to the OEM specification.
Reinstallation of Wedge Bolts
When inspecting racking, or anytime it’s noticed, if a wedge bolt has been pulled out of the plate by a forklift strike by 1" or less, you may attempt to retighten the knot to OEM specification. First, follow your procedure for notification and documentation of racking damage. Before starting, inspect the columns, beams, cross bracing, and shelving for damage and order repair systems as needed to replace the damaged parts.
The following is critical for the safe installation of
repair systems using pallet rack anchors, such as those from Damotech:
- Never re-use anchor holes (in most cases)
- Drill holes at correct diameters using ANSI carbide-tipped bits of the same diameter as the anchor.
- Use the OEM-supplied wedge bolts for your repair.
- Drill new holes
- Make sure to tighten the anchor bolt notch to the OEM torque specifications. If proper torque cannot be achieved, relocate a new anchor.
OSHA Pallet Rack Anchor Requirements
OSHA does not have specific guidelines for anchoring pallet racks. However, the general clause of the Occupational Safety Health Act requires employers to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards. Proper installation of pallet racks is essential for safety, and posts and braces must be anchored according to OEM specifications to avoid safety violations. OSHA does not specify the exact standards themselves. They use industry standards for their references from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard MH16.1-2023. OSHA can levy heavy fines for violations.
It is best to consult with knowledgeable professionals to avoid all the headaches, fines, safety hazards, and dangers of improper pallet rack anchoring.
Whether a skyscraper or a pallet rack, it’s only as good as its anchor to the foundation. Damotech creates a stronger, safer environment that resists loads of daily use, occasional accidents, and seismic motion by thoroughly inspecting, replacing, or installing racking anchors.

- Top 12 Largest Warehouses in North America (Size, Tech & Safety)
- Top 100 Warehouse Safety Quotes for Toolbox Talks, Posters & Meetings
- Costco’s Supply Chain Strategy: Decoding Its Warehousing Approach
- Minimum Distances Between Pallets, Rack Systems & Building Structures
- IKEA Warehouses: Efficient Warehousing and Distribution Strategies








