Pallet racks are metal structures designed to support the goods in a warehouse or an industrial facility. Various factors, such as the type of products, order of inventory retrieval, space/cost limitations, and turnaround time, can impact the selection of a rack type.
Selecting the right pallet racking type and design
Selecting the type of rack to use in your warehouse can be challenging. A well-designed warehouse pallet racking system can help optimize available space and throughput while ensuring operational productivity and safety.
This article will explore the key differences between industrial rack systems, highlighting the pros and cons of each type. Whether you are in the market for a new rack system or simply looking to understand the available options better, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of rack types.
What are the different types of warehouse racks?
There are two main categories of racking systems commonly used in warehouses: static and dynamic. Each category has several types of systems. Each type of racking system has unique advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these differences can help you select the best racking system for your specific needs.
In this blog, eight types of racking systems will be discussed:
Static pallet rack types
Dynamic pallet rack types

Static Racking System Designs
A static pallet racking system is built to be stationary (pallets do not move once put in place or retrieved). Static racking systems are commonly used due to their adjustability and typically have lower costs than dynamic systems.
Static racks include selective (single-deep), double-deep, cantilever, and drive-in/drive-through pallet racks.
1. Selective Pallet Racks (Single-Deep)
Selective (single-deep) pallet racks are the most commonly used pallet rack systems in warehouses. They are cost-efficient and the least expensive compared to other rack types. These racks offer adjustability and are an ideal option for storing different kinds of products.
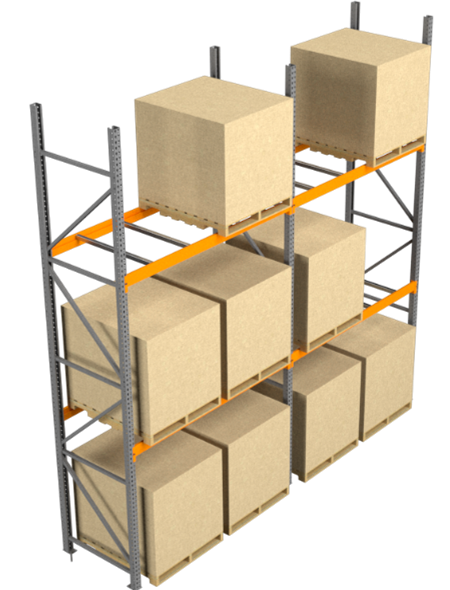
Figure 1: Selective rack (single-deep)
The rack’s beam heights and bay widths can be adjusted to meet the requirements of various sizes and weights of pallets. They are often configured in back-to-back rows to conserve aisle space.
Advantages:
- Inexpensive compared to other rack types.
- Immediate access to all storage locations.
- Easy to modify (engineering approval required).
Disadvantages:
- Apart from setups with very narrow aisles (VNA), not very dense as they require multiple aisles.
- Costly for high-volume storage; many racks and ample warehouse space required.
2. Double-Deep Pallet Racks
Double-deep racking systems are similar to selective (single-deep) racking systems in their core components, but they have a key difference: they feature an added second row. This design enhances storage capacity, making it suitable for items with high inventory levels.
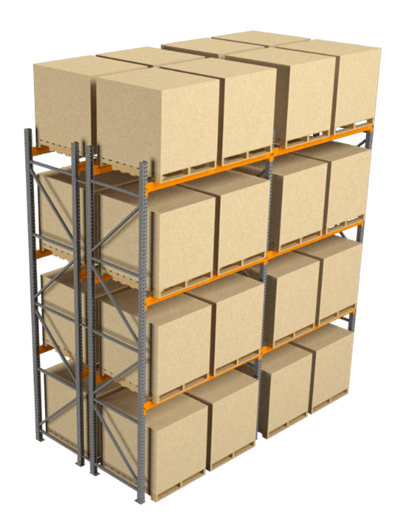

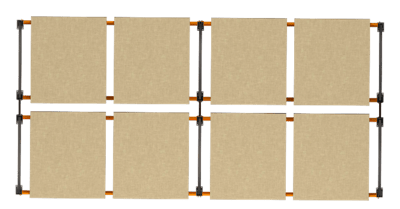
Figures 2 and 3: Double-deep rack (side and top view)
Double-deep racks are mainly used for cold storage to maximize space and cost or dry storage where expiry is not a concern. This racking requires a specialized deep-reach forklift truck for loading and unloading due to its two-load-depth configuration.
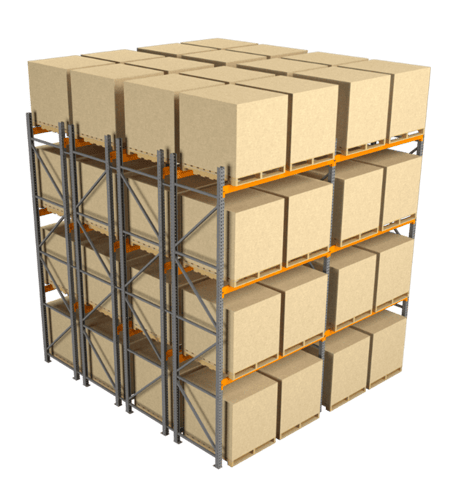

Figure 4: Back-to-back double-deep racks
Advantages:
- Compared to single-deep racking systems, double-deep racks have increased storage density.
- Cost efficient – Fewer aisles while allowing more storage capacity at a lower cost.
Disadvantages:
- Require deep-reach forklift trucks to access pallets on the second row.
- Reduced accessibility – Access to rear pallets becomes more challenging, as it requires moving the front pallets first, leading to slower inventory retrieval times.
3. Cantilever Pallet Racks
Cantilever racks are specialized racks providing a space-efficient storage solution for long and bulky items, like PVC pipes, steel sheets, and lumber. They are constructed from vertical columns, braces, arms, and bases. Depending on their design, cantilever racks can be used for light to heavy-duty applications.
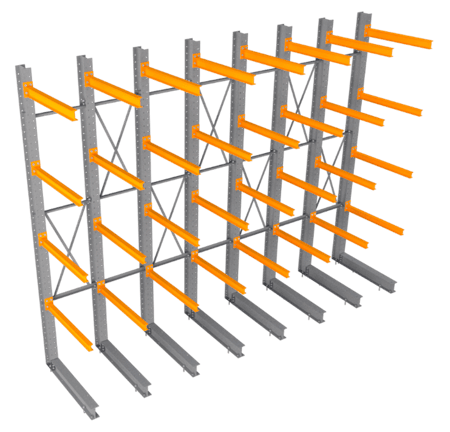
Figure 5: Cantilever rack
Cantilever racks are assembled in two possible configurations: single or double-sided. Single-sided racking is only accessible from one side and is typically built against a wall. Double-sided racks provide direct pick access from both aisles, back-to-back, where the same column is used with arms on both sides. These racks are frequently found in plumbing supply warehouses, lumber yards, and shipping yards.
Advantages:
- Ideal for storage of long/bulky loads
- Variable storage capacity, from light to heavy-duty products.
- Quick storage and easy retrieval of products.
Disadvantages:
- High capital cost compared to other storage racks.
- Considerable floor space required for safe forklift access.
4. & 5. Drive-In and Drive-Through Pallet Racks
Drive-in and drive-through (sometimes called drive-thru) rack systems offer high-density storage capacity by maximizing warehouse space. These racks are called “drive-in/through” because forklifts must drive directly into the rack structure to access and place pallets on the rails that span the depth of the structure.
Drive-in pallet racks have a single entry and exit point on one side of an aisle. Drive-thru racks have an entry and exit point on opposite ends of the system, allowing forklifts to enter the rack structure from the front or the back.
Drive-in and drive-through bays are often arranged side-by-side to maximize the warehouse floor space and height, and each bay-level depth can hold multiple pallets. Considering the high storage capacity it provides, it is a highly cost-effective racking system compared to the other racks.
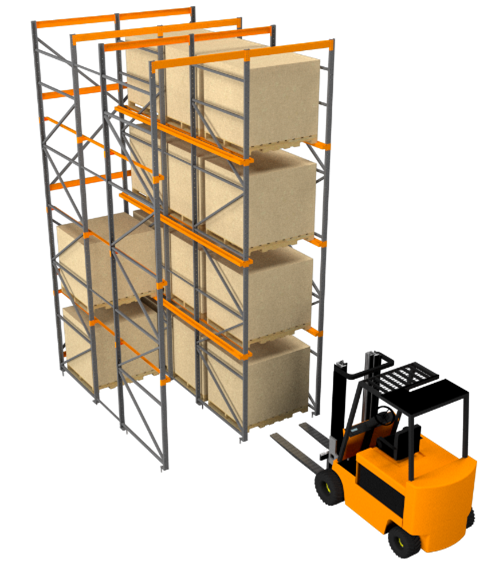

Figure 6: Drive-in rack
A drive-in rack system operates in LIFO (last in, first out) stock rotation: the last pallet deposited in a slot will be the first to be unloaded. Since the forklift has one access point for each aisle for loading/unloading the pallets, you can install the rack against a wall. Due to its low rotation, this system is common in cold storage units and freezers.
By contrast, a drive-through rack system operates in FIFO (first in, first out) stock rotation: the first pallet deposited on the racking will be the first to be unloaded. The forklift can access both ends of the aisle, one for loading and another for unloading. The racks must be installed in the warehouse aisles, not against a wall.
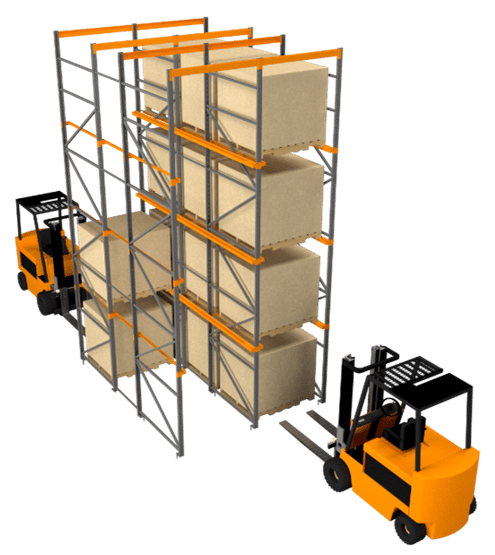

Figure 7: Drive-through rack
Advantages:
- Warehouse space optimization.
- Cost-effective, high-density rack systems.
- Significantly less square footage required compared to selective pallet racks.
Disadvantages:
- Not ideal for facilities with many different products.
- Prone to damage since forklifts enter the rack.
- Not flexible in design; standard pallet sizes required.
Dynamic Racking System Designs
There are two types of dynamic rack systems: gravity racks and mobile racks. Gravity pallet racks, either Push Back or Pallet Flow, are designed with levels on an incline, and the racks are resting on wheeled carts or rollers. Mobile racks are selective single-deep racks mounted on wheels. They operate using a motorized unit, which allows the rack’s rows to be moved on slab-level rails.
1. Push Back Pallet Racks
A push back racking system is a high-density storage system with a stock rotation method similar to a drive-in racking system: LIFO (last in, first out). The main difference is that the pallets are loaded onto a gravity-fed wheeled cart system that rolls on an inclined rail in each lane. The forklift has one access point for each location for loading/unloading pallets.

Figure 8: Push back rack
To load, place a pallet on a rolling cart. The cart is then pushed back into the system each time an additional pallet is loaded. Due to the incline, the carts roll down to the aisle position and are held in place by the structure when a pallet is removed. The incline makes this rack system significantly faster to load and unload than a drive-in rack system.
Advantages:
- High-density storage capacity.
- Lower rack damage because forklifts do not enter rack structures.
Disadvantages:
- Costly compared to a drive-in pallet rack system.
- Higher maintenance and lifetime service costs for the rolling cart system.
2. Pallet Flow Pallet Racks
Pallet flow racking is a high-density storage system with pallets on roller conveyors. The stock is rotated on a FIFO (first in, first out) basis, similar to a drive-through rack system. The difference is that pallet flow racks are operated on an inclined gravity-induced roller system, and the forklifts cannot enter the racking system.

Figure 9: Pallet flow rack
Pallet flow racking systems have forklift access at two ends of the system, one for loading and the other for unloading. The pallets are loaded onto rollers at one end, which are moved by gravity to the front of the system for easy unloading.
Advantages:
- Increased worker productivity - reduced travel time to load/unload.
- Quick inventory turnover through FIFO (first in, first out).
Disadvantages:
- High initial capital investment.
- Regular maintenance of the braking system.
- Pallets must always be in good condition to prevent jams.
Carton flow racks are essentially pallet flow racks, but they are used for picking up small boxes instead of pallets. They are mostly integrated with selective racks to create a dynamic hybrid system to support both pallets on the upper levels and picking on the bottom levels. Both carton flow and pallet flow racks share functionality but serve different purposes.

Figure 10: Carton flow rack
3. Mobile Pallet Racks
Mobile racking is a compact storage rack on a rail system attached to the floor. The racks are on wheels that move along the floor rails and are aligned with each other to save space.
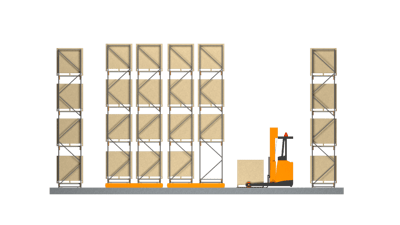
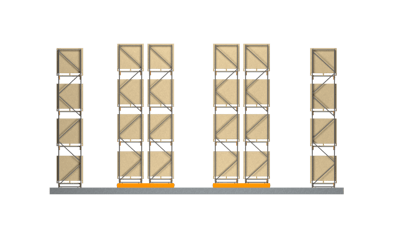
Figures 11 and 12: Mobile racks
Adjacent rows are moved using a motorized unit to access an aisle. It is possible to incorporate various safety features (such as audible or visual alarms) into the system to minimize risks of collapse and workplace incidents. Mobile racking is an ideal storage solution in situations with space restrictions.
Advantage:
- Space-efficient since it requires less space than selective racking.
Disadvantages:
- High installation and maintenance costs.
- Typically requires increased safety measures.
- Additional time required to move rows before accessing pallets.
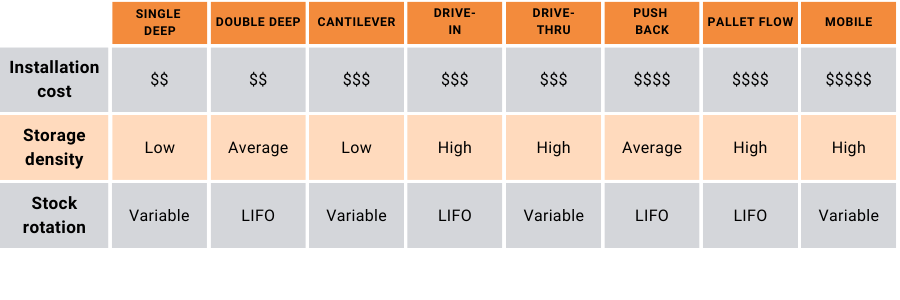
Comparison of All Industrial Pallet Rack System Types
The table below compares all the rack types discussed based on different selection criteria.
Pallet Rack Type Selection Based on Warehouse Requirements
In conclusion, pallet rack systems are a crucial component in warehouse storage and organization of goods. There are several categories and types of pallet rack systems, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages and best suited for specific merchandise and storage needs.
Carefully choose the right pallet racking system for your warehouse needs. Products, warehouse space, and cost should be considered when making your selection. With the right pallet racks in place, you can create an effective warehousing system and improve the productivity of your warehouse.
Remember that regardless of the type of racks you choose, they must always be in safe working condition. To assist with this, Damotech offers a variety of free tools that can help you assess the condition of your racking systems and identify any potential hazards. By utilizing these resources, you can take the necessary steps to ensure that your pallet racks are safe and reliable for your employees and your business.
Content References
- https://www.srs-i.com/blog/advantages-disadvantages-cantilever-racking/
- https://www.mazzellacompanies.com/learning-center/warehouse-racking-pallet-rack-systems-different-types-design/
- https://www.mskcanada.com/en/blog/5-advantages-of-high-density-industrial-mobile-shelving
- https://www.super-racking.com/info/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-mobile-shelves-51912413.html
- https://mallardmfg.com/pallet-flow-racking-vs-simple-selective-pallet-rack-when-why
- https://www.ar-racking.com/en/news-and-blog/storage-solutions/storage-racking-solutions/types-of-industrial-racking-for-the-warehouse-classification-and-characteristics
- https://arnoldmachinerymh.com/pallet-racking/push-back/
- https://www.warehousestoragesolutions.com/push-back-pallet-racking-what-is-it
- https://www.commander.ca/product-push-back-pallet-racking/
- https://gujratsteel.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-drive-in-racking-systems/
- https://www.ar-racking.com/en/news-and-blog/storage-solutions/storage-racking-solutions/differences-between-drive-in-and-drive-through-racking
- https://www.ar-racking.com/en/news-and-blog/storage-solutions/storage-racking-solutions/types-of-industrial-racking-for-the-warehouse-classification-and-characteristics
- https://ecseco.com/blog/single-vs-double-deep-selective-rack-which-is-the-best-option-for-you/
- https://phindustry.com/2016/08/07/top-benefits-of-single-deep-pallet-racking/
- https://vestrainet.weebly.com/blog/selective-racking-advantages-and-disadvantages
- https://advancestorageproducts.com/4-advantages-to-utilizing-double-deep-selective-pallet-racking-in-your-warehouse
- https://www.mskcanada.com/en/blog/5-advantages-of-high-density-industrial-mobile-shelving
- https://ecseco.com/blog/stackable-racking-types-and-use-cases/
Figure References
- Figure 7: https://www.cssyes.com/product/twinlode-drive-in-pallet-rack/
- Figure 10: http://3dlogistic.ca/carton-flow/









