Pallet rack beams are a critical component of your racking system, bearing the weight of valuable inventory and ensuring operational efficiency. These mission-critical components are engineered to handle specific loads, but there are some aspects that, if neglected, can lead to structural failure. This article outlines the best practices regarding pallet racking beams that every warehouse manager should know in order to maintain a safe and efficient operation.
How Critical are Pallet Rack Beams?
There are three essential facts about pallet rack beams, the most prominent being that they hold the weight of your inventory between the upright frames of your pallet rack system. Yet, there are two less obvious roles beams play that are often overlooked.
First, they provide horizontal rigidity to the racking system, preventing lateral displacement or swaying under seismic activity and dynamic forces, such as forklift impacts. Second, they enhance the torque resistance of the upright. Pallet rack beams contribute to the overall structural stability by bracing the upright columns and reducing the risk of deformation or buckling under concentrated vertical loads at lower levels.
Maintaining the structural integrity of your beams is critical to the safety and efficiency of your warehouse. Keep reading to ensure you address all the necessary details and best practices that prevent beam failure.
Correct Installation of Pallet Rack Beams
Proper Pallet Rack Beam Spacing
Racking beams should be specified by a qualified engineer familiar with the design and load dynamics of pallet racking systems. If the size or weight of your inventory changes or if beam requirements are altered, an engineer must be consulted. Upon analysis, they may be able to specify different vertical beam spacings for your system.
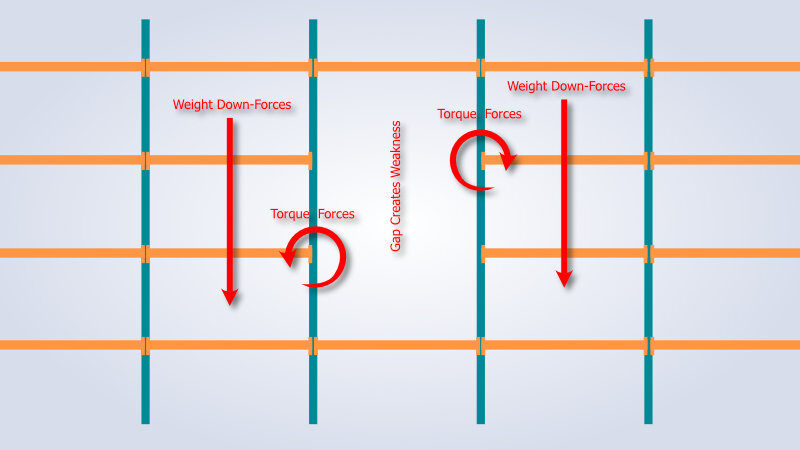
Any modifications to beam spacing patterns should be carried out under engineering supervision with proper documentation, as changes to the spatial configuration directly impact the overall load capacity and stability of the racking system. Larger beam gaps can reduce horizontal rigidity, causing the upright columns to experience more torque and potentially compromise the structural integrity of the entire system.
Never adjust the beam spacing without adhering to the original design specifications or consulting a qualified engineer. Any changes to the “as-built” configuration must be carefully evaluated to ensure compliance with safety standards and performance requirements.
The pallet racking beam clip or engagement pin system, as specified by the OEM manufacturer, should be used to connect your beam to the columns unless an alternate engineered connection has been approved for use. Inspect the beam clip or pin to ensure it is fully and properly engaged. On roll-formed uprights, a safety clip or pin is often used in addition to the standard beam clip to ensure that the beam-to-upright connection does not disengage accidentally.
The RMI (Rack Manufacturers Institute) specifies that beam-locking devices are required to prevent pallet rack beams from accidental dislodgement caused by forklift activity. These locking devices may include bolts, pins, hooks, or other approved devices that satisfy the RMI-specified 1,000-pound uplift requirement. Ensure that each beam connector is properly aligned and adequately engaged with the upright columns. Disengaged pins or clips can lead to racking beams failing and cascading damage to facility personnel or other racking structures.
Additionally, do not assume that a bigger bolt is a better replacement for the original clips. The beam clips or pins were specifically engineered for your racking system, even engineered to fail under certain conditions to ensure the overall safety of the system. Never use an aftermarket bolt to replace a missing j-pin or safety clip unless it has been approved by a qualified engineer. These small components play a crucial role in the safe operation of your entire warehouse.
Proper Loading and Labeling
Each pallet rack beam has a specified maximum load capacity determined by the engineer who designed the racking system, which must be displayed. Pallet rack beams should be labeled with the maximum weight capacity, and the label should be placed on the front of the beam, facing the aisle. Alternatively, it is recommended by RMI (Rack Manufacturers Institute) to display system load capacity plaques in conspicuous locations at the end of each row to indicate the maximum allowable load for each beam configuration in that aisle.
Loads must also be evenly distributed and balanced across the beams. Typically, if your warehouse management system (WMS) includes this functionality, your loading software should provide you with an even load distribution pattern. If you do not have this functionality, a visual inspection of the inventory can help you determine whether the load distribution is even.

Proper Decking
When decking is used, it should be installed according to the engineered specifications of your pallet rack system. While some applications may not require decking, when it is utilized, options like wire mesh decking or wooden decking should be carefully evaluated. Ensure the decking material and configuration comply with the structural engineering requirements of your system and adhere to local building codes for fire safety and load capacities. Always consult a qualified engineer to confirm that the selected decking system is suitable for your specific inventory, pallet types, and intended application.
Additionally, pallet sizes should align with the dimensions and load specifications outlined in the original system design. It is recommended that pallets overhang the front and back beams by 2 to 4 inches. Any deviation from these parameters could compromise the structural integrity of the racking system. Decking or pallet failures can cause inventory to shift or fall, potentially leading to rack damage, safety hazards, and injuries to facility personnel. Proper decking and pallet use are essential for maintaining operational safety and protecting both your assets and workforce.
Pallet Rack Beam Types
Pallet Rack Beam Shapes
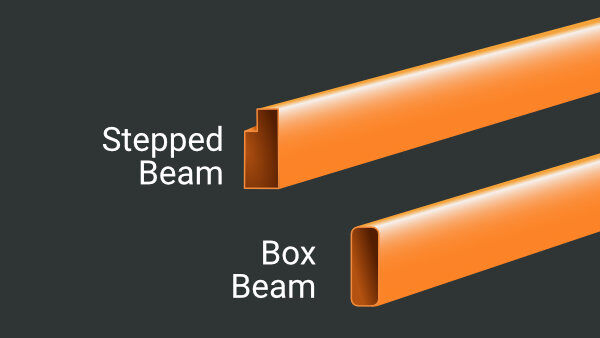
The following are two of the common beam shapes: box and step. Box beams do not have an interior step slot, and if wire decking is used, it is secured on top of these beams. Step beams have a step that is used as a slot to support crossbars and wire decking. It is critical to adhere to the beam shape specified in your original system design, as substituting a different shape can compromise the beam’s load capacity and structural integrity. Safety should never be compromised—any damaged pallet rack beams must be replaced promptly to maintain system integrity and safety compliance.
Pallet Rack Beam Length
Pallet rack beams come in various lengths, and selecting the appropriate length is essential for accommodating pallets. Typically, a beam should allow for a 3" clearance around the pallet. As the length of the beam increases, the beam gauge also needs to be increased to ensure the beam can support the load. The engineer calculates the total load, and it is critical to ensure that these specifications are adhered to in order to maintain the system’s structural integrity.
Pallet Rack Beam Size
The type of steel and thickness used in your pallet rack beams will affect the load-bearing capacity. Since steel weights and gauges are not visually identifiable, ensure you always refer to the specifications provided in the original engineering plans. RMI (Rack Manufacturers Institute) recommends against mixing pallet rack beams from different manufacturers. Ensure that all replacement or new beams meet the original engineering specifications.
Damage to Pallet Rack Beams
Forklift Damage
Damage to your pallet rack beams can come from several sources, with the most common being:
Forklifts and loading vehicles: Damage can occur more frequently when the loading vehicle is too large for the aisle width. Impacts from forklifts and loading vehicles can damage pallet rack beams, deform or disengage the safety pins or beam connectors, and cause severe dents or shearing of the beams. Damage can occur more frequently when the loading vehicle is too large for the aisle width.
Damage can occur to the bay being loaded and to bays across the loading bay that are backed into by forklifts. Ensure that proper material handling equipment is used for your racking system design and that it is operated by trained professionals. Have drivers report all impact incidents, regardless of whether they are minor or major.
Improper Loading
Overloading is a common form of damage in this category. It can cause beam deformation (bending). While slight deformation is acceptable, it becomes hazardous when the deformation exceeds the maximum allowable limit due to excess weight. This deformation can be measured and should not exceed L/180, where “L” is the length of the beam.
Unauthorized Modifications
Some warehouse staff may not understand the importance of the precise positioning of pallet rack beams as a qualified engineer would. For example, you may work in the building, but it doesn’t mean you fully understand the architectural design. Some may assume that the safety pins used on racking systems allow beams to be moved to new locations without issue.
In some cases, racking beams are even removed to accommodate traffic or larger inventory. These modifications alter the torque forces in the upright and can lead to upright failure. This type of damage doesn’t show up as visible bends or dents but affects the original engineering design, creating a weakness similar to that caused by unclipped or damaged beams. Ensure your staff is trained to never move a beam without proper consultation by a qualified engineer.

Seismic Events
Earthquakes can cause twisting and torsion in your racking system. After such events, damage may occur to beam connectors, safety pins, and column pinholes. From a safety perspective, it is crucial to be proactive and schedule a thorough professional inspection as soon as possible following a seismic event.
Corrosion
Corrosion is particularly hazardous to the small pins and clips that secure pallet rack beams in place. The load-bearing capacity of your system depends on whether these components do not deteriorate due to rust or corrosion. The beams themselves can also rust when exposed to harsh conditions. Additionally, special attention should be given to the very lowest section of the upright frame, as corrosion can affect the welds that connect the baseplates to the upright.
If racking beams are mounted close to the floor, special attention should be given to the welds connecting the beam to the beam clips and the upright column. Be aware that corrosion may not be easily spotted from the front and could require close inspection from different angles to detect early signs of damage. Galvanized components should be used in areas where rust is common.
Upright Damage
Pallet rack beams rely on a secure connection to the upright. Uprights can sustain damage from twisting during the attachment or removal process, forklift impacts, or seismic events. When repairing, both the uprights and pallet rack beams must be thoroughly assessed. A trained professional from Damotech can assist in navigating the complexities of this process, ensuring that the components are adequately inspected and conform to all engineering standards.
Inspection Techniques
Once your racking system has been properly installed, regular inspections should be conducted to ensure that there is no severe damage. Comprehensive inspections should be conducted by a professional at regularly scheduled intervals and documented for reference. Your racking inspection logs can be used in the event of an OSHA inspection.
Informal inspections
You and your team should perform ongoing informal inspections. Workers should be encouraged to identify damages and report issues. Damotech’s inspection checklist can be used for these informal inspections.
Training your staff to recognize and report damages helps maintain a safe warehouse environment. Informal inspections should never replace formal inspections, which are conducted by trained professionals in accordance with RMI standards. Damotech offers a free safety inspection poster that can be ordered and displayed in your facility to educate your warehouse personnel on identifying and reporting damaged racking.

Official Inspections
RMI standards dictate that formal inspections of pallet racks should be performed routinely, depending on your pallet rack system’s load capacity and usage patterns. Damotech has qualified, trained inspectors who can perform these inspections for you.
Look for all the damages listed below. Take note and document the specific location if any of these conditions exist:
- Bent or downward beam deflection. Report deflection if the deflection distance exceeds the beam span’s length divided by 180.
- Missing, disengaged, or corroded beam clips.
- Load Labels that are missing or unreadable.
- Beam connectors disengaged from the column, bent, or showing weld failures.
- Dents, cuts, and cracks in pallet rack beams or beam connectors.
- Improper loading that doesn’t conform to the load standards of your racking system.
- Missing pallet rack beams (beams that have been moved or removed for any reason).
- Pro Tip: Check behind-beam connectors and front/rear beams; unload them if necessary to inspect. Use a lift to inspect higher points. Report all temporary repairs.
Pallet Rack Beam Repair
Beam Repair
Typically, pallet rack beams should not be repaired but replaced with identical OEM parts as specified in the original engineering design. Minor issues with locking pins and connectors may be addressed according to the repair methods selected by the manufacturer or a qualified engineer, which can then be performed by the manufacturer or a trained technician.
The beam should be offloaded when damage is detected, and inventory should be moved. Severe damage may compromise the integrity of the entire upright. An experienced, trained inspector or a qualified engineer from Damotech can provide guidance on the necessary steps for repair or replacement.
Upright Repair
The repair of uprights often directly impacts your pallet rack beams. Upright repairs affect beams in two ways. First, upright damage can also damage the beams. The punch holes on beams can be sheared, bent, or twisted. Never reinstall a damaged beam into a damaged upright. Always repair the uprights and beams before reinstalling them.
An experienced inspector can detect any damage done to your upright columns. Upright damage often occurs just above or below a beam, requiring the replacement of the upright column section where the beam is attached. If the beam attachment to the repair part is done without engineering oversight, the structural integrity of the entire system may be compromised.
ANSI standards for pallet racking systems and beams
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) establishes specific guidelines and regulations for the use of industrial components, including pallet racking systems. Below are the key rules directly applicable to pallet racking systems and beams.
According to ANSI MH16.1:
- The racking system operator is responsible for maintaining and repairing the storage systems; i.e., the person in charge of the pallet racking system is to be held responsible for any misconduct in the process.
- Upon visible damage, the pertinent portions of the rack shall be unloaded immediately and removed from service by the user until the damaged portion is repaired or replaced, i.e., when you inspect a component to be damaged or broken, you immediately unload the damaged section of racking and tag it out of service until the damage is repaired or replaced. You’re not allowed to use the system until the damaged component has been replaced/repaired and reinstalled into the system.
- Any beam with visible deformation or cracking of the beam end connectors should be unloaded and replaced. Be sure beams are fully engaged and installed with proper safety locks. When you detect visible deformation or cracking in the beams, you need to remove the load and replace the damaged component immediately. You can utilize the system after repairing the component and engaging it in the system.
- When handling beams, you must adhere to a safe deflection limit. The maximum allowed deflection can be calculated by dividing the beam’s length by 180.
These regulations apply to all types of pallet racking systems, regardless of the kind of steel (cold-formed or hot-rolled), and to both movable and non-movable racking systems.
Key Takeaways on Racking Beams
-
Ensure pallet racks are installed correctly, adhering to the manufacturer’s specifications, and have their capacities displayed.
-
Inspect beams informally and formally at regular intervals.
-
Rely on Damotech for inspections, repairs, and the installation of all engineered parts to avoid improper modifications that may compromise the system’s structural integrity and load capacity.
-
Recognize that beams are a key component of any safe and efficient warehouse operation.
Contact Damotech if you have any questions or need help with keeping your personnel and warehouse safe and efficient.











